- Bank Of India Saving Account Interest Rate
- Savings Account Interest Rates India
- Bank Of India Saving Account Interest Rate Calculator
In India there are different heads of income; viz., income from Salary, House property, Capital gain, Business & Profession and Income from other sources. Today we are here to discuss only a small part i.e. Interest Income of one of the head of income i.e. “Income from other sources”. You’ll learn about Taxation on Interest income including the important tax deductions available thereon.
Central Bank of India FD Premature Withdrawal. Central Bank of India charges a penalty of 1% interest rate on premature withdrawal of deposits more than Rs 5 lakhs. However, there is no penalty in case of account renewal for a longer term as compared to the initial deposit period. Central Bank of India – FAQs. Saving Deposit Interest Income: Saving Deposit Interest is the income earned on any saving deposit scheme as defined under The Banking Regulation Act. In simplest words, it is the interest that you earn on the balance in your savings bank account. Fixed Deposit Interest Income: FD Interest is the income earned on any fixed deposit scheme.
Income from Other Sources: Meaning
- The rate is applicable to the BOI savings account prduct which has a free Internet Banking facility with free funds transfer through internet banking. It has unlimited Internet & ATM transactions however you will be charged Rs.20/- per month if you do not maintain the minimum balance per month.
- For account holders with cheque book facility, without cheque book facility, and for a no-frills savings account, the interest rate is 4%. What are the proofs to be submitted for address verification while opening a Central Bank of India savings account?
- Citizens Charter of Union bank of India Right to. Salary Account Demat Account Saving Account. General General Interest Rate Interest Rates.

Income from other sources is a head of income which includes the entire income amount which doesn’t fall in any of the other income heads. This may include but not limited to income like gift amount, interest income, lottery, awards, etc.
Interest Income: Meaning
Interest income is an income which an individual earns from:
- Bank deposits,
- Deposits in other financial institution and
- Organizations like post office, trust, etc.
Taxation of Interest Income in India
Interest income in the hands of an individual is taxed under normal slab rates. Thus, assuming an individual has no other income then the first Rs.250,000 would be tax free. After that, the amount shall be taxed at the rate of 5% or 20% or 30% depending on the income tax slab rate respectively.
Before going into benefits and tax deduction for the said income; we need to check and understand different types of interest income. Let me walk you through the details of the same.
Types of Interest Income
So, have a look at the different types of interest income that you can earn from different sources in India.
Bank Of India Saving Account Interest Rate
1. Saving Deposit Interest Income:
Saving Deposit Interest is the income earned on any saving deposit scheme as defined under The Banking Regulation Act. In simplest words, it is the interest that you earn on the balance in your savings bank account.

2. Fixed Deposit Interest Income:
FD Interest is the income earned on any fixed deposit scheme. Simply stating, it is the interest earned on deposits which are made for a fixed period of time as defined under The Banking Regulation Act.
3. Recurring Deposit Interest Income:
RD interest is the income earned on any recurring deposit scheme. RD scheme is the deposit wherein a person agrees to deposit fixed amount at regular intervals for a fixed period of time, as defined under The Banking Regulation Act.
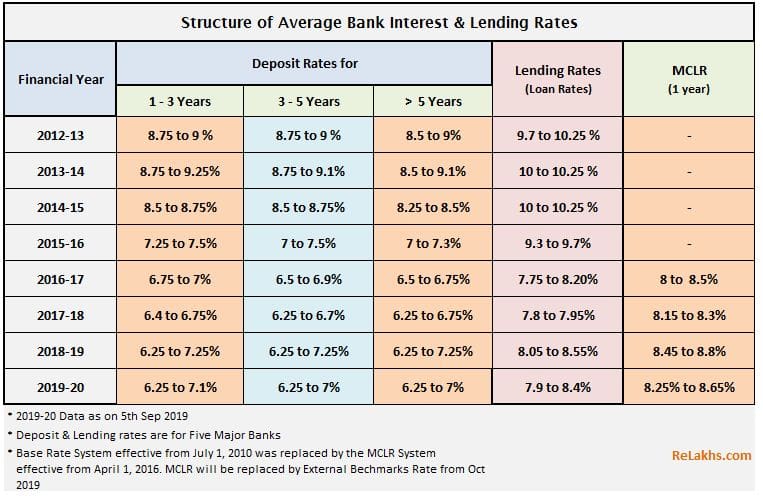
4. Post Office Deposit Interest Income:
In India there are a number of Post Office Saving Schemes for individuals to invest. So, you also earn income on these Post Office Deposit Schemes as defined under Post Office regulation.
Section 80TTA: Income Tax Deduction on Interest Income
Under Income Tax Act, Section 80TTA lays down the tax deduction rule for interest income.
As per Section 80TTA, an individual can claim a deduction of interest income up to Rs.10,000 if the interest income is earned through saving deposit scheme alone.
Section 80TTB: Tax Deduction on Interest Income for Senior Citizens
Also, in the Budget 2019 there was a new section introduced for Senior citizens i.e. Section 80TTB. Under Section 80TTB an individual who is 60 years or more can claim extra tax deduction of up to Rs.50,000 on interest income earned. The interest income may be from saving account or fixed deposit or post office deposit scheme.
However, if you as a senior person claim deduction under Section 80TTB you can’t claim Section 80TTA deduction.
No doubt, the Government offers additional tax benefits to senior citizens on interest and other incomes as well. And, that’s really good for our senior members.
Thus, only saving deposit interest income (senior citizens exception applies) has the benefit of tax exemption. Whereas other interest income like fixed and recurring deposit are subject to tax under section 194A at the rate of 10%.
You may also like: TDS on Commission or Brokerage U/s 194H
Savings Account Interest Rates India
Taxation of Interest Income: The Bottom Line
This was all about interest income and how it is taxed in India. If you have any other important points to add here, do let us know in the comments.
Bank Of India Saving Account Interest Rate Calculator
On a general basis, interest incomes are subject to tax under Section 194A at the rate of 10% at the time of payment. Banks deduct tax on fixed deposit income i.e. TDS on Interest only after a specified limit of Rs.10000 normally and Rs.50000 limit for senior citizens.
Moreover, it is an individual’s responsibility to add the interest income (savings+FD+other) to their total income while filing Income tax return.
Following two situations may be arise:
- You need to deduct appropriate tax which might be over 10% (already deducted) or
- You may have to claim refund in case excess was deducted earlier as TDS.
You may also like to visit Best Mobile Banking Apps in India
Few people try to skip the interest income to avoid taxes thereon, this is not correct. Whatever way, you must include the interest income under the head “Income from Other Sources” in your ITR. Then, calculate the tax payable or refund as applicable.

Feel free to discuss for any queries on interest income and its taxation in India. You may also put your feedback or share views on any financial topic on our active discussion forum.